The First education centre of India: A Historical Overview
Education has always played a pivotal role in shaping the development and progress of civilizations. In India, a country known for its rich cultural heritage, the history of education can be traced back to ancient times. The quest for knowledge and the dissemination of learning have been integral parts of India’s cultural ethos, and the establishment of the first school in India marked a significant milestone in the country’s educational journey.

The origins of formal education in India can be traced back to the ancient Vedic period, which dates back to around 1500 BCE. During this period, education was primarily centered around the Vedas, which were a collection of sacred texts containing a vast repository of knowledge on various subjects, including philosophy, theology, mathematics, astronomy, and medicine. The Vedas were taught in gurukuls, which were residential schools where students lived with their gurus (teachers) and received holistic education.
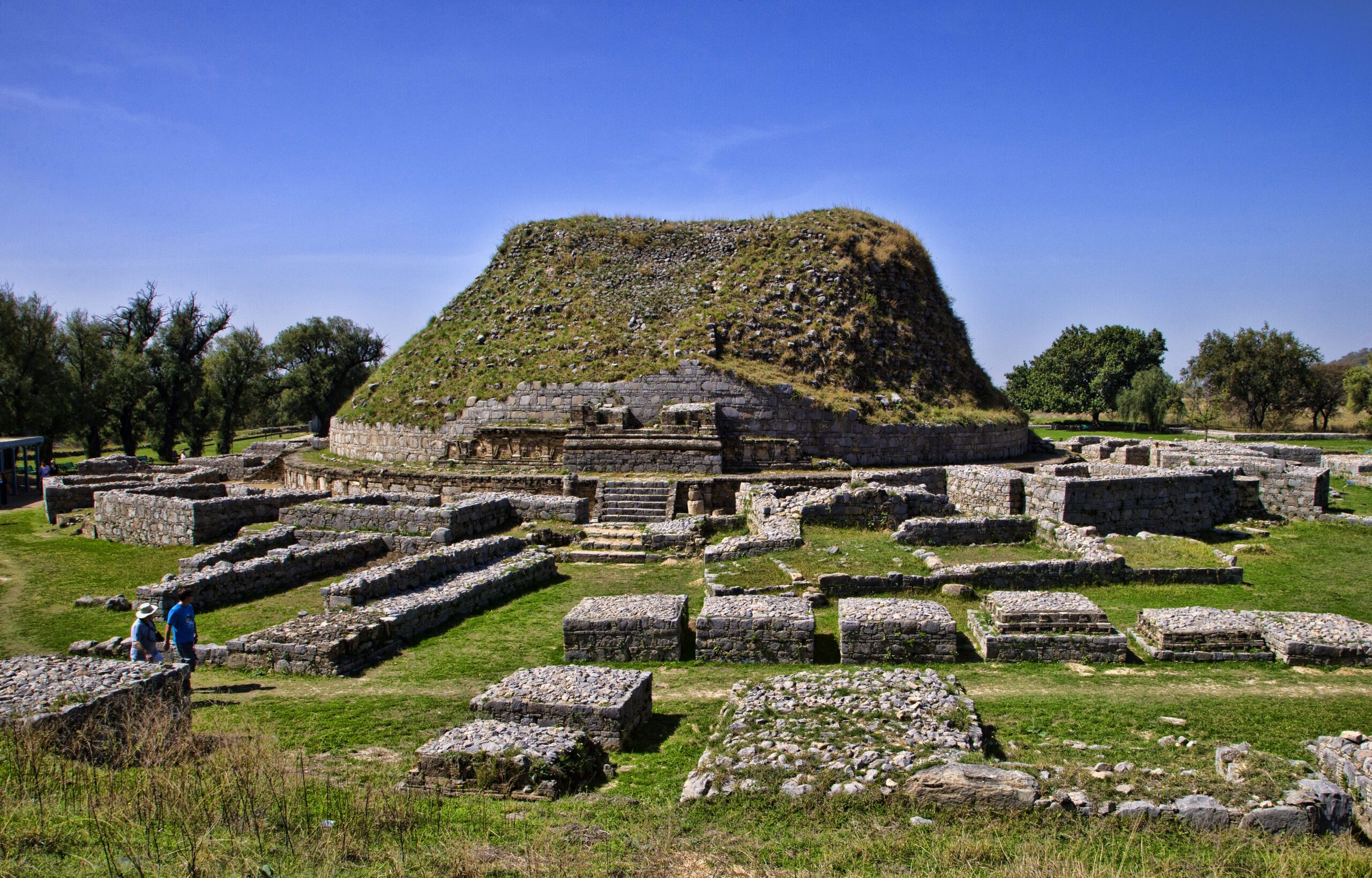
One of the earliest documented evidence of a school in India can be found in Taxila, an ancient city in present-day Pakistan, which was a renowned center of learning during the 6th century BCE. Taxila was home to one of the world’s oldest universities known as Takshashila University, which attracted scholars and students from across the Indian subcontinent, Central Asia, and other regions. The university offered a wide range of subjects, including philosophy, mathematics, medicine, politics, and military strategy, and had a well-organized system of education with a rigorous curriculum and examinations.

In the southern part of India, the ancient city of Nalanda, located in present-day Bihar, was another prominent center of learning during the ancient period. Nalanda University, established around the 5th century CE, was known for its excellence in the fields of Buddhist studies, philosophy, and logic. It attracted scholars and students from all over Asia, including China, Tibet, Korea, and Central Asia, making it one of the most renowned educational institutions of its time.
During the medieval period, the focus of education in India shifted to the establishment of madrasas, which were Islamic centers of learning. These madrasas provided education on Islamic studies, Arabic, Persian, and other subjects. They played a crucial role in spreading Islamic education and culture in India and were instrumental in shaping the intellectual and cultural landscape of the country.
The British colonial rule in India, which lasted for nearly two centuries, had a significant impact on the country’s educational system. The British introduced a western-style education system in India, which included the establishment of English-medium schools and universities, modeled after the British educational system. The first English-medium school in India, the Hindu College, was established in Calcutta (now Kolkata) in 1817, followed by the establishment of other institutions such as the Elphinstone College in Bombay (now Mumbai) and the Madras Christian College in Madras (now Chennai).
After India gained independence from British rule in 1947, the country’s education system went through significant reforms to make education accessible to all citizens. The focus shifted towards universal education, with the establishment of primary schools, secondary schools, and higher education institutions across the country. Today, India has one of the largest education systems in the world, with a vast network of schools, colleges, and universities catering to the educational needs of millions of students.
In conclusion, the first school in India can be traced back to the ancient Vedic period, with gurukuls being the early centers of education. Over time, India witnessed the establishment of renowned universities like Takshashila and Nalanda, which were centers of excellence in learning. The British colonial rule introduced western-style education, and after gaining independence, India underwent significant educational reforms. Today, India has a robust education system